Physical Address
304 North Cardinal St.
Dorchester Center, MA 02124
Physical Address
304 North Cardinal St.
Dorchester Center, MA 02124


Chinese startup DeepSeek has released DeepSeek-V3. According to the benchmarks they shared, this is now the most capable open-source large language model currently available. It even achieves performance comparable to leading closed-source models even though it was trained on a budget of just $5.6 million—a fraction of what major tech companies typically spend.
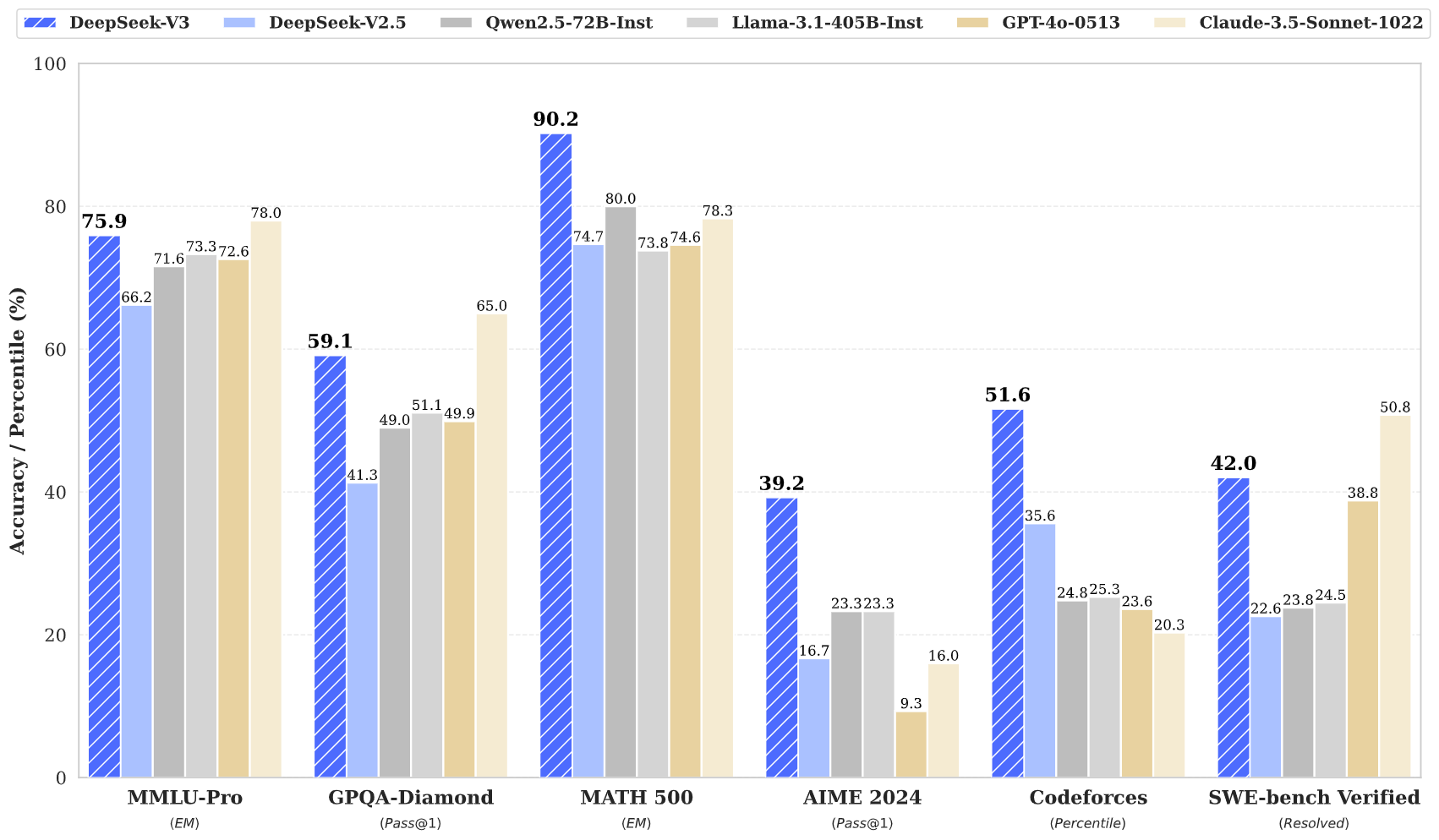
The team’s achievement is particularly noteworthy given the company’s size and the budget they were able to accomplish this with. “DeepSeek making it look easy with an open weights release of a frontier-grade LLM trained on a joke of a budget,” noted Andrej Karpathy, a founding member of OpenAI, in a post on X. The secretive startup is entirely self-funded through its hedge fund operations, and has not sought any external investment.
DeepSeek (Chinese AI co) making it look easy today with an open weights release of a frontier-grade LLM trained on a joke of a budget (2048 GPUs for 2 months, $6M).
For reference, this level of capability is supposed to require clusters of closer to 16K GPUs, the ones being… https://t.co/EW7q2pQ94B
— Andrej Karpathy (@karpathy) December 26, 2024
Zoom In: At the technical core of DeepSeek-V3 is a Mixture-of-Experts (MoE) architecture with 671 billion total parameters, though only 37 billion are activated for each token. This selective activation approach, combined with innovative training techniques, allows the model to achieve high performance while maintaining efficiency. The model particularly shines in mathematical reasoning and coding tasks, where it sometimes outperforms established players like OpenAI and Anthropic. Here’s the technical paper with all the details.
The company says it used several techniques, including FP8 mixed precision training and efficient pipeline parallelism, which significantly reduced computational requirements. This efficiency becomes even more remarkable when compared to Meta’s LLaMA 3, which required approximately 30.8 million GPU hours for training.
Why it Matters: DeepSeek spent just $5.57 million to train their model, while Meta reportedly invested over $500 million to train Llama 3. If we compare GPU hours, DeepSeek-V3’s 2.78 million hours is dramatically less than Llama 3’s 30.8 million hours. That is an efficiency gain of roughly 11x.
These numbers become even more striking when considering that some of the largest AI training clusters being built today utilize around 100,000 GPUs, suggesting training costs potentially reaching into billions of dollars. DeepSeek achieved its results using just 2,048 H800 GPUs over approximately two months, demonstrating that efficient architecture and training methods can dramatically reduce the resources needed for cutting-edge AI development.
Yes, But: The achievement isn’t without controversy. There are valid questions to be asked about the model’s training data. When prompted, the model often claims that it is ChatGPT…
DeepSeek-V3 seems to be trained on ChatGPT outputs. It answers like this about 1/5 of my trials (you need to ask it with the lower case “w“, that seems to be important). a legal pathway for western startups to indirectly train on ChatGPT outputs? https://t.co/BT5diEAcZa pic.twitter.com/hP6OFiSGy0
— Samuel Müller (@SamuelMullr) December 27, 2024
Some have accused the company of including data generated from proprietary models like GPT-4o or Claude 3.5 Sonnet. If true, this would constitute a violation of terms of service agreements—a practice referred to as ‘ToS laundering.’
Global Implications: Still, the implications of DeepSeek-V3’s success is so much more than a technical achievement—it is a major geopolitical signal. China’s ability to still produce a frontier-grade AI model under the resource constraints imposed by US embargo highlights shows just how quickly their AI ecosystem is advancing.
“The bitter lesson of Chinese tech: they work while America rests, and catch up cheaper, faster & stronger,” observed Alexander Wang, CEO of Scale AI, highlighting the shifting dynamics in global AI development.
It is quite fitting that DeepSeek, China’s leading LLM lab, releases its latest model V3 on Christmas.
– on-par with GPT-4o & Claude 3.5 Sonnet
– trained w/10x less computeThe bitter lesson of Chinese tech: they work while America rests, and catch up cheaper, faster & stronger https://t.co/GcrDgtXETz pic.twitter.com/pkpyISUOAh
— Alexandr Wang (@alexandr_wang) December 26, 2024
Despite these concerns, DeepSeek-V3’s open-source availability on Hugging Face aligns with a broader push by many in the industry to democratize AI capabilities. Its auxiliary loss-free load-balancing strategy and multi-token prediction (MTP) techniques have set new benchmarks for training efficiency and inference speed.
The Big Picture: For the AI industry, DeepSeek-V3 represents a potential paradigm shift in how large language models are developed. The achievement suggests that with clever engineering and efficient training methods, frontier capabilities in AI might be achievable without the massive computational resources previously thought necessary.
As the field digests these developments, DeepSeek-V3’s success may prompt a reevaluation of established approaches to AI model development. As open-source models continue to narrow the gap with their closed-source counterparts, companies may need to reassess their strategies and value propositions in an increasingly competitive landscape.